Resistor color codes helps to read resistance, tolerance and voltage. Other than these three values, there is another important parameter required, for using the resistor in a circuit. This is power rating of a resistor.It is very important to use correct power rated resistor in the circuit to prevent the circuit from damaging.
What is the meaning of power rating?
Resistor power rating can be defined as the maximum power a resistor can handle safely without any damage. We know that, resistor dissipates the excess energy in form of heat. Power rating indicates the maximum heat a resistor can dissipate safely. Increasing the power more for few percent than rating, will burn the resistor.
How resistors are rated?
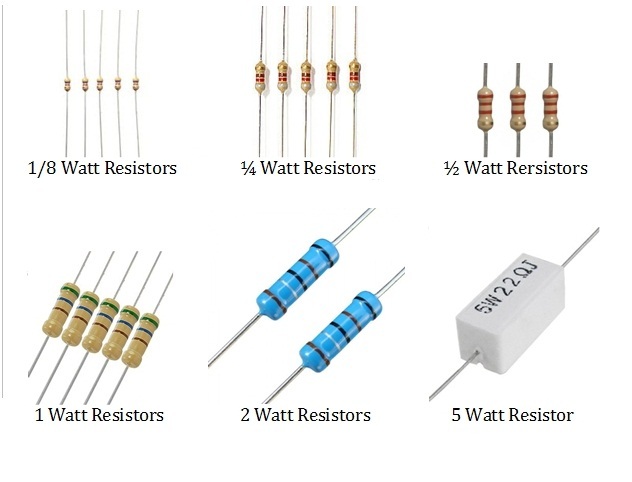
The resistor power rating is rated in watts, which are units of power. Hence it is also termed as wattage. Generally, larger the resistor more power it can handle. As the wattage of the resistor increases cost also increases. Resistors generally start from 1/8th watt to many kilo watts.Resistor wattage can be noticed by seeing the size of the resistor.
Resistors with high wattage are called power resistors. Below is the figure showing resistors with their wattage.
How to determine wattage of a resistor?
Electrical power is given as P=V x I Where v is voltage I is current From Ohm’s Law, we have V = I × R Where R is resistance Therefore P = I2 × R And P = V2 / R Hence the power dissipation in a resistor can be calculated using any of the following standard equations
Power P = V × I P = I2 × R P = V2 / R
Here is example to calculate the resistor rating to be used in a circuit. Consider a circuit powering a led with a source voltage of 12v and resistance of 800 ohms. Now calculate what wattage resistor can be used in the circuit? We know V= 12v ,R=800 ohms.Now calculating the current I=V/R=12/800 = 0.015=15 mA current. Thus power dissipated by the resistor is calculated using P= 12x15x10-3 =0.18 watts Hence a 1/4th watt resistor must be used here. Using 1/8th watt resistor will damage the circuit.
Power Resistors
Resistors that are designed to handle high power are called power resistors. Resistors with power rating of at least 5W come under power resistors. The material used for construction of power resistors must be of high thermal conductive in nature. Power resistors often come with heat sink which helps them in dissipation of heat.
Wire wound power resistors
Wire wound power resistors are common, but they can also be found in other types. If Nichrome alloy based wire wound resistors are used with proper non-conductive enamel paint, they can withstand temperatures up to 4500C.
Grid Resistors
Grid Resistors are used to withstand large amounts of currents . They can withstand a current up to 500 Amps and can have a resistance values as low as 0.04 Ω. The construction of Grid Resistors includes two electrodes with large metal stripes connected between them in the form of a matrix. Grid resistors are used as grounding resistors, brake resistors and harmonic filters for electric substations.
Water Resistors
The construction includes tubes which carry saline solution with electrodes connected at both ends of the tube. The concentration of saline solution or salt water will determine the resistance. Because of the presence of water in the tubes, water resistors provide large heat capacity, which in turn result in high power dissipation.
SMD Power Resistors
Power resistors can also be made in the form of Surface Mounted Devices. Because of their small size, the power dissipation capacity of SMD resistors is less than grid type resistors and water resistors. Usually the power dissipated by SMD resistors is in the order of few Watts. The range of power dissipated by different types of power resistors are as follows
SMD Resistors 5 W or less Helical Wound 50 W or less Edge Wound 3.5 KW or less Grid Resistors 100 KW or less Water Resistors 500 KW or less
Applications of Power Resistors
Power resistors are used in applications where we need to dissipate large power. Some of the applications of Power resistors are Comment * Name * Email * Website
Δ





![]()